9. Experiment on orthogonal Learning#
#import packages
import hdmpy
import numpy as np
import random
import statsmodels.api as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import colors
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
9.1. Simulation Design 1#
# Set seed
np.random.seed(0)
B = 100
Naive = np.zeros( B )
Orthogonal = np.zeros( B )
for i in range( 0, B ):
n = 100
p = 100
beta = ( 1 / (np.arange( 1, p + 1 ) ** 2 ) ).reshape( p , 1 )
gamma = ( 1 / (np.arange( 1, p + 1 ) ** 2 ) ).reshape( p , 1 )
mean = 0
sd = 1
X = np.random.normal( mean , sd, n * p ).reshape( n, p )
D = ( X @ gamma ) + np.random.normal( mean , sd, n ).reshape( n, 1 )/4 # We reshape because in r when we sum a vecto with a matrix it sum by column
# DGP
Y = D + ( X @ beta ) + np.random.normal( mean , sd, n ).reshape( n, 1 )
# single selection method
r_lasso_estimation = hdmpy.rlasso( np.concatenate( ( D , X ) , axis = 1 ) , Y , post = True ) # Regress main equation by lasso
coef_array = r_lasso_estimation.est[ 'coefficients' ].iloc[ 2:, :].to_numpy() # Get "X" coefficients
SX_IDs = np.where( coef_array != 0 )[0]
# In case all X coefficients are zero, then regress Y on D
if sum(SX_IDs) == 0 :
Naive[ i ] = sm.OLS( Y , sm.add_constant(D) ).fit().summary2().tables[1].round(3).iloc[ 1, 0 ]
# Otherwise, then regress Y on X and D (but only in the selected coefficients)
elif sum( SX_IDs ) > 0 :
X_D = np.concatenate( ( D, X[:, SX_IDs ] ) , axis = 1 )
Naive[ i ] = sm.OLS( Y , sm.add_constant( X_D ) ).fit().summary2().tables[1].round(3).iloc[ 1, 0]
# In both cases we save D coefficient
# Regress residuals.
resY = hdmpy.rlasso( X , Y , post = False ).est[ 'residuals' ]
resD = hdmpy.rlasso( X , D , post = False ).est[ 'residuals' ]
Orthogonal[ i ] = sm.OLS( resY , sm.add_constant( resD ) ).fit().summary2().tables[1].round(3).iloc[ 1, 0]
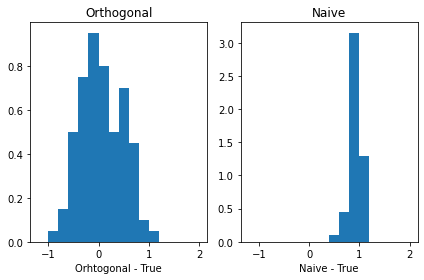
Orto_breaks = [-1.2, -1, -0.8, -0.6, -0.4, -0.2, 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6, 1.8, 2]
Naive_breaks = [-0.6, -0.4, -0.2, 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1, 1.2]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex= True, tight_layout=True)
# We can set the number of bins with the `bins` kwarg
axs[0].hist( Orthogonal - 1 , range = (-2, 2), density = True , bins = Orto_breaks )
axs[1].hist( Naive - 1, range = (-2, 2), density = True , bins = Naive_breaks )
axs[0].title.set_text('Orthogonal')
axs[1].title.set_text('Naive')
axs[0].set_xlabel( 'Orhtogonal - True' )
axs[1].set_xlabel( 'Naive - True' )
Text(0.5, 0, 'Naive - True')
9.2. Simulation Design 2#
# Set seed
np.random.seed(0)
for i in range( 0, B ):
n = 100
p = 100
beta = ( 1 / (np.arange( 1, p + 1 ) ** 2 ) ).reshape( p , 1 )
gamma = ( 1 / (np.arange( 1, p + 1 ) ** 2 ) ).reshape( p , 1 )
mean = 0
sd = 1
X = np.random.normal( mean , sd, n * p ).reshape( n, p )
D = ( X @ gamma ) + np.random.normal( mean , sd, n ).reshape( n, 1 )/4 # We reshape because in r when we sum a vecto with a matrix it sum by column
Y = D + ( X @ beta ) + np.random.normal( mean , sd, n ).reshape( n, 1 )
# single selectin method
r_lasso_estimation = hdmpy.rlasso( np.concatenate( ( D , X ) , axis = 1 ) , Y , post = True )
coef_array = r_lasso_estimation.est[ 'coefficients' ].iloc[ 2:, :].to_numpy()
SX_IDs = np.where( coef_array != 0 )[0]
if sum(SX_IDs) == 0 :
Naive[ 0 ] = sm.OLS( Y , sm.add_constant(D) ).fit().summary2().tables[1].round(3).iloc[ 1, 0 ]
elif sum( SX_IDs ) > 0 :
X_D = np.concatenate( ( D, X[:, SX_IDs ] ) , axis = 1 )
Naive[ i ] = sm.OLS( Y , sm.add_constant( X_D ) ).fit().summary2().tables[1].round(3).iloc[ 1, 0]
resY = hdmpy.rlasso( X , Y , post = True ).est[ 'residuals' ]
resD = hdmpy.rlasso( X , D , post = True ).est[ 'residuals' ]
Orthogonal[ i ] = sm.OLS( resY , sm.add_constant( resD ) ).fit().summary2().tables[1].round(3).iloc[ 1, 0]
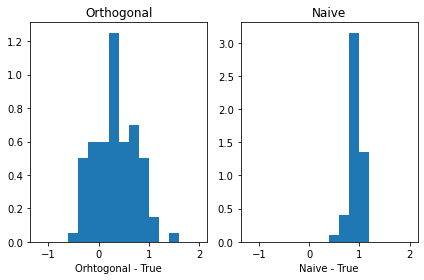
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex= True, tight_layout=True)
# We can set the number of bins with the `bins` kwarg
axs[0].hist( Orthogonal - 1 , range = (-2, 2), density = True , bins = Orto_breaks )
axs[1].hist( Naive - 1, range = (-2, 2), density = True , bins = Naive_breaks )
axs[0].title.set_text('Orthogonal')
axs[1].title.set_text('Naive')
axs[0].set_xlabel( 'Orhtogonal - True' )
axs[1].set_xlabel( 'Naive - True' )
Text(0.5, 0, 'Naive - True')