11. Heterogenous Wage Effects#
We use US census data from the year 2012 to analyse the effect of gender and interaction effects of other variables with gender on wage jointly. The dependent variable is the logarithm of the wage, the target variable is female (in combination with other variables). All other variables denote some other socio-economic characteristics, e.g. marital status, education, and experience. For a detailed description of the variables we refer to the help page.
This analysis allows a closer look how discrimination according to gender is related to other socio-economic variables.
install.packages("librarian", quiet = T)
librarian::shelf(hdm, quiet = T)
data(cps2012)
str(cps2012)
also installing the dependency ‘BiocManager’
These packages will be installed:
'hdm'
It may take some time.
also installing the dependencies ‘iterators’, ‘foreach’, ‘shape’, ‘Rcpp’, ‘RcppEigen’, ‘glmnet’, ‘checkmate’, ‘Formula’
'data.frame': 29217 obs. of 23 variables:
$ year : num 2012 2012 2012 2012 2012 ...
$ lnw : num 1.91 1.37 2.54 1.8 3.35 ...
$ female : num 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 ...
$ widowed : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ divorced : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ separated : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ nevermarried: num 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 ...
$ hsd08 : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ hsd911 : num 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ hsg : num 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 ...
$ cg : num 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 ...
$ ad : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ mw : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ so : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ we : num 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
$ exp1 : num 22 30 19 14 15 23 33 23.5 15 15.5 ...
$ exp2 : num 4.84 9 3.61 1.96 2.25 ...
$ exp3 : num 10.65 27 6.86 2.74 3.38 ...
$ exp4 : num 23.43 81 13.03 3.84 5.06 ...
$ weight : num 569 626 264 257 257 ...
$ married : logi TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE ...
$ ne : logi TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE ...
$ sc : logi TRUE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE FALSE ...
# create the model matrix for the covariates
X <- model.matrix(~-1 + female + female:(widowed + divorced + separated + nevermarried +
hsd08 + hsd911 + hsg + cg + ad + mw + so + we + exp1 + exp2 + exp3) + +(widowed +
divorced + separated + nevermarried + hsd08 + hsd911 + hsg + cg + ad + mw + so +
we + exp1 + exp2 + exp3)^2, data = cps2012)
X <- X[, which(apply(X, 2, var) != 0)] # exclude all constant variables
demean<- function (x){ x- mean(x)}
X<- apply(X, 2, FUN=demean)
dim(X)
# target variables, index.gender specifices coefficients we are interested in
index.gender <- grep("female", colnames(X))
y <- cps2012$lnw
- 29217
- 116
The parameter estimates for the target parameters, i.e. all coefficients related to gender (i.e. by interaction with other variables) are calculated and summarized by the following commands:
# this cell takes a minute to run
effects.female <- rlassoEffects(x = X, y = y, index = index.gender)
result=summary(effects.female)
result$coef
| Estimate. | Std. Error | t value | Pr(>|t|) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| female | -0.154923281 | 0.050162447 | -3.08843149 | 2.012161e-03 |
| female:widowed | 0.136095484 | 0.090662629 | 1.50111997 | 1.333245e-01 |
| female:divorced | 0.136939386 | 0.022181700 | 6.17352970 | 6.678200e-10 |
| female:separated | 0.023302763 | 0.053211795 | 0.43792476 | 6.614408e-01 |
| female:nevermarried | 0.186853483 | 0.019942393 | 9.36966209 | 7.276511e-21 |
| female:hsd08 | 0.027810312 | 0.120914496 | 0.22999982 | 8.180919e-01 |
| female:hsd911 | -0.119335040 | 0.051879684 | -2.30022682 | 2.143537e-02 |
| female:hsg | -0.012889780 | 0.019223188 | -0.67053290 | 5.025181e-01 |
| female:cg | 0.010138553 | 0.018326505 | 0.55321800 | 5.801141e-01 |
| female:ad | -0.030463745 | 0.021806103 | -1.39702838 | 1.624050e-01 |
| female:mw | -0.001063439 | 0.019191770 | -0.05541119 | 9.558109e-01 |
| female:so | -0.008183343 | 0.019356818 | -0.42276282 | 6.724683e-01 |
| female:we | -0.004226129 | 0.021168404 | -0.19964324 | 8.417596e-01 |
| female:exp1 | 0.004935259 | 0.007804275 | 0.63237886 | 5.271393e-01 |
| female:exp2 | -0.159519328 | 0.045299884 | -3.52140699 | 4.292632e-04 |
| female:exp3 | 0.038450579 | 0.007861100 | 4.89124680 | 1.001992e-06 |
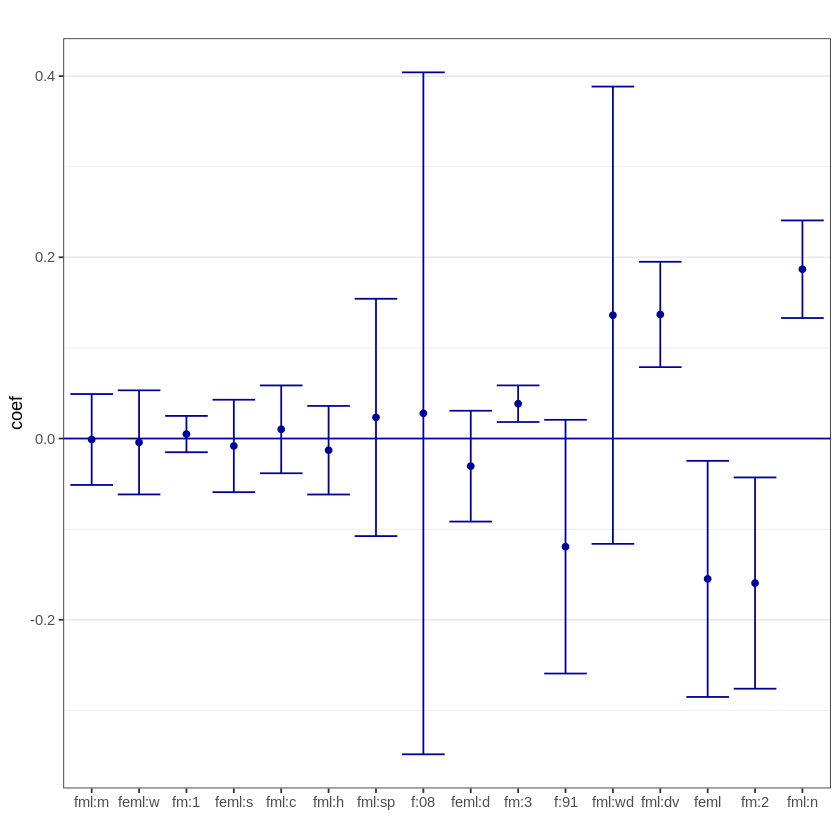
Now, we estimate and plot confident intervals, first “pointwise” and then the joint confidence intervals.
pointwise.CI <- confint(effects.female, level = 0.90)
pointwise.CI
plot(effects.female, level=0.90) # plot of the effects
| 5 % | 95 % | |
|---|---|---|
| female | -0.237433164 | -0.072413398 |
| female:widowed | -0.013031271 | 0.285222239 |
| female:divorced | 0.100453736 | 0.173425037 |
| female:separated | -0.064222851 | 0.110828376 |
| female:nevermarried | 0.154051166 | 0.219655800 |
| female:hsd08 | -0.171076335 | 0.226696960 |
| female:hsd911 | -0.204669525 | -0.034000554 |
| female:hsg | -0.044509111 | 0.018729551 |
| female:cg | -0.020005866 | 0.040282971 |
| female:ad | -0.066331593 | 0.005404103 |
| female:mw | -0.032631091 | 0.030504214 |
| female:so | -0.040022474 | 0.023655789 |
| female:we | -0.039045055 | 0.030592798 |
| female:exp1 | -0.007901632 | 0.017772149 |
| female:exp2 | -0.234031007 | -0.085007650 |
| female:exp3 | 0.025520220 | 0.051380937 |
Warning message:
“Ignoring unknown aesthetics: width, h”
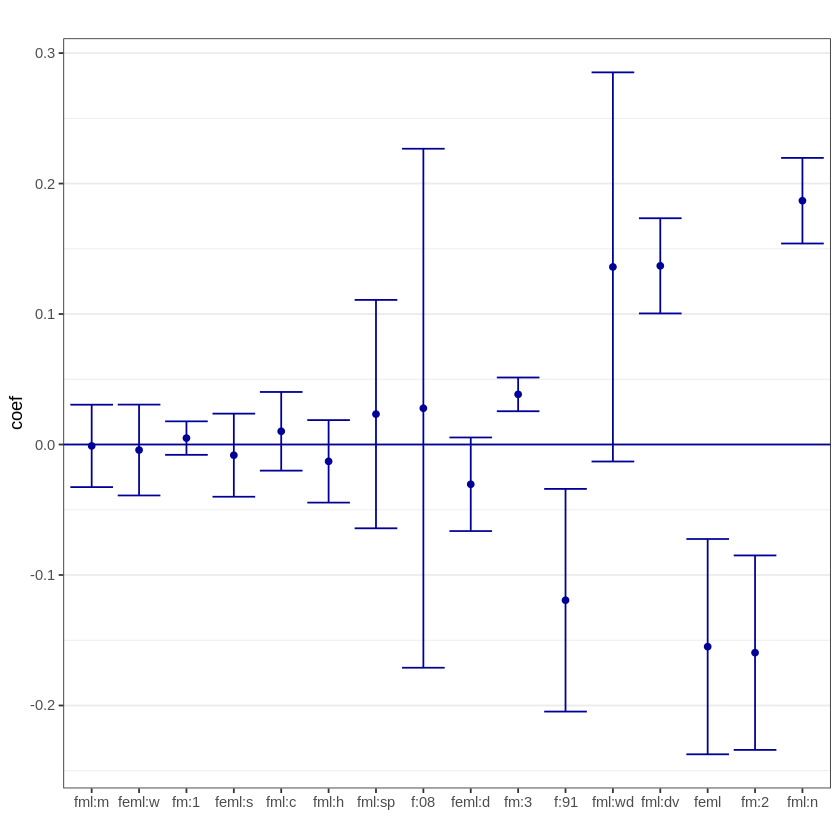
Finally, we compare the pointwise confidence intervals to joint confidence intervals.
joint.CI <- confint(effects.female, level = 0.90, joint = TRUE)
joint.CI
plot(effects.female, joint=TRUE, level=0.90) # plot of the effects
| 5 % | 95 % | |
|---|---|---|
| female | -0.28721730 | -0.02262927 |
| female:widowed | -0.12010118 | 0.39229214 |
| female:divorced | 0.07792288 | 0.19595589 |
| female:separated | -0.10967329 | 0.15627881 |
| female:nevermarried | 0.13215504 | 0.24155193 |
| female:hsd08 | -0.35426488 | 0.40988550 |
| female:hsd911 | -0.26149507 | 0.02282500 |
| female:hsg | -0.06251119 | 0.03673163 |
| female:cg | -0.03907505 | 0.05935216 |
| female:ad | -0.09254849 | 0.03162100 |
| female:mw | -0.05200948 | 0.04988260 |
| female:so | -0.05997736 | 0.04361068 |
| female:we | -0.06254002 | 0.05408776 |
| female:exp1 | -0.01541738 | 0.02528790 |
| female:exp2 | -0.27787565 | -0.04116301 |
| female:exp3 | 0.01793445 | 0.05896671 |
Warning message:
“Ignoring unknown aesthetics: width, h”